-
Street Name, NY 38954

How to Prevent Falls after Age 70 By 8 Things?

Mrs. Rose is 69 years old. She usually wears reading glasses, but she has not changed them for more than a decade. She suffers from hypertension and diabetes. She usually takes medicine on time, but often needs to take antihypertensive drugs, hypoglycemic drugs, and other drugs at the same time.
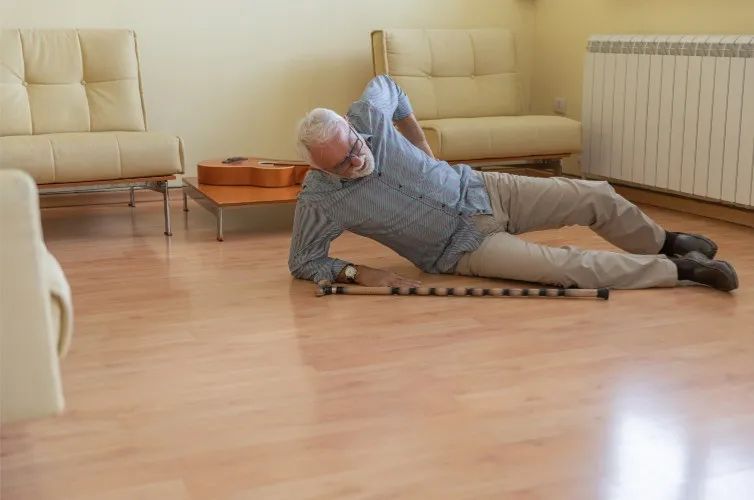
One morning at the beginning of this year, Mrs. Rose was in a hurry to go to the bathroom. When she got there and tried to turn on the light switch, she suddenly felt dizzy and weak in her limbs. She hurriedly held on with her hands.
As there was no handrail in the bathroom, Mrs. Ruth’s hand was on the smooth wall tiles and she slipped and fell.
Fortunately, the family heard the noise and rushed to the hospital and dialed an ambulance to send her to the hospital.
After diagnosis and treatment, Mrs. Rose’s ankle fracture gradually recovered after resting at home for 4 months.
After inquiry, it was found that Mrs. Rose had repeatedly experienced dizziness and unsteady feet when she got up to go to the bathroom in the morning without taking medicine.
Be Alert to Falls in the Elderly
With age, the body functions of the elderly deteriorate, muscle strength is weakened, balance is reduced, gait is abnormal, and sensory and motor function is reduced, all of which lead to an increased risk of falls.
Some diseases can also increase the risk of falls in older adults, such as cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, and eye diseases. In addition, complex environmental factors can also increase the risk of falls in older adults.
How to Prevent Falls in the Elderly
1. Check your eyesight regularly
Early detection and treatment of vision-related eye diseases are important for preventing falls.
The main eye diseases that increase the risk of falls in the elderly include refractive errors (myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism), cataracts, hemianopia, glaucoma, and macular degeneration.
Among them, senile cataract is the most common cause of vision loss.
The elderly should have their eyesight checked once a year and correct and improve their vision by wearing glasses or undergoing surgery when necessary.
2. Prevent Osteoporosis
Elderly people with osteoporosis are more prone to falls, and after falling, it is prone to fractures, which can affect health and quality of life.
Osteoporosis prevention is key. For dietary management, first, prioritize calcium-rich foods like dairy products, soy-based foods, and nuts, with milk and dairy products being the primary source of dietary calcium. Second, incorporate vitamin D-rich options to enhance calcium absorption and utilization, such as seafood (salmon, herring), egg yolks, mushrooms, and cheese.
In addition, moderate sun exposure can also promote the skin to synthesize vitamin D.
3. Choose the Right Walking Aid
A cane is the most common walking aid, which can help the elderly maintain body balance, support part of their weight, and reduce the burden on their legs.
The commonly used crutches are walking sticks and walkers. If you often feel unsteady on your feet or sometimes feel weak in your legs, consider using walking sticks. It should be remembered that you should not use trekking poles instead of walking sticks.
Elderly people with weakness in the lower limbs or unable to bear weight due to leg disease should use a walking aid.
How to choose A Suitable Crutch for yourself
① Grip should be comfortable.
② The bottom of the stick should be slip-resistant.
③ The length should be appropriate, the crutch should stand “as tall” as the person, and the handle height should be level with the naturally hanging wrist.
4. Choose the right shoes
Shoes play a very important role in keeping the elderly physically stable.
Try on shoes before you buy them and keep the following four points in mind.
① The size should be appropriate.
Big shoes don’t fit the feet, like slippers, can’t provide enough support for the feet, can make people lose balance, and the feet tire easily. Too small shoes will wear the feet, uncomfortable to wear, not only affecting the feet to feel the ground, which is not conducive to body control, but also affecting blood circulation.
② Hardware and software should be appropriate.
While a soft sole can increase comfort, it can make it difficult to maintain your center of gravity when walking. On the other hand, wearing hard soles can make it difficult for your feet to judge the ground and make it less slippery.
③ The soles should be non-slip.
The deep and many tread patterns can increase the friction between the shoe and the ground, and the anti-slip performance is better. Shoes with shallow tread patterns are easy to slip when wearing.
④ The heel height should be moderate.
For the elderly, the height of the heel should not be higher than 2cm, otherwise it will affect the position of the body’s center of gravity, change the posture of the foot when walking, and increase the risk of falling.
5. Change positions slowly
The elderly should move slowly rather than fast in daily life. If they turn around, turn their head, get up or get up too quickly, they are likely to fall due to dizziness and blurred eyes, especially when getting up and getting up from a chair.
When getting up, the elderly should do “three 30-second” to avoid discomfort caused by rapid changes in position.
① After waking up, open your eyes while lying flat, wait for 30 seconds to adapt to the process from sleep to wakefulness.
② Slowly sit up, wait for 30 seconds, turn your neck, and move your limbs.
③ Move your legs to the edge of the bed, with your feet on the ground, sit quietly for 30 seconds, and if the reaction is normal, get out of bed and walk.
6. Increase physical exercise
Appropriate physical exercise for the elderly is very helpful in improving balance, controlling weight, increasing bone density and muscle strength, improving body flexibility, etc., which helps reduce the risk of falls.
For the elderly, Tai Chi and Ba Duan Jin are more suitable sports and have been proven to effectively prevent falls in the elderly.
① Brisk walking:
Based on natural walking, swing your arms, raise your head and chest, relax your neck and shoulders, gently tighten your abdomen, slightly retract your lower jaw, look straight ahead, and naturally twist your body with the midline as the axis.
The specific key points of swinging arms are to relax your hands like holding an empty fist, bend your elbows naturally to about 90 degrees, and swing your arms naturally back and forth with the shoulder joints as the axis. When swinging upward, your hands should not exceed your shoulders, and when swinging downward, your hands should not exceed your waist.
The reasonable stride of brisk walking is generally height multiplied by 0.45. The speed and time vary from person to person. It is best to breathe slightly faster, but be able to speak normally.
It is generally recommended that the elderly can brisk walk 3 to 5 days a week, 30 to 50 minutes a day, and the step frequency should be 120 to 150 steps/minute.
② Stepping on the steps:
Stand facing the steps, with your toes pointing forward, and step the entire sole of your left foot on the steps. Keep your body balanced, use your left thigh and hips to lift your right leg off the ground, then slowly lower it back to the ground, and then retract your left leg; repeat the above steps with your right leg.
Repeat the above steps 10 times.
Old people should choose the step height according to their situation; generally, about 10 cm is appropriate.
7. Safe use of drugs
Many drugs have adverse reactions that affect the consciousness, spirit, and gait balance of the elderly, and increase the risk of falls in the elderly, such as antidepressants, hypnotics, anti-cardiovascular disease drugs, and dopamine drugs, etc. However, the elderly should not refuse to take medicine when they are sick.
Medication for the elderly should be
① Follow the doctor’s advice and use the medicine properly.
② Understand the adverse reactions of the medicine and consult the doctor regularly for evaluation.
③ Take a rest after taking the medicine and pay attention to the reaction.
8. Improve the home environment.
Home is considered a “haven”, but as the elderly age, their balance and reaction abilities gradually decline. Many seemingly safe homes may be full of traps for them.
Can limiting going out or reducing activities after a fall in the elderly reduce the occurrence of falls?
Elderly people will have a series of psychological problems after falling, especially after multiple falls, they will have “fear of falling”; that is, they are always worried about falling again, so they often consciously limit their activities or hesitate when doing activities. As a result, their motor ability and balance ability will further decline, which in turn increases the risk of falling, leading to a vicious cycle.
Therefore, limiting activities or reducing going out after a fall will not reduce the occurrence of falls in the elderly.
How to improve the “fear of falling” of the elderly ?
- The elderly should establish correct cognition. It is normal to worry about falls, and the elderly should realize the seriousness of injuries caused by falls and the possible harm, and take the initiative to prevent falls instead of throwing out the baby with the bathwater, such as reducing physical activities, going out, and socializing.
- The elderly can learn and understand the knowledge of fall prevention through books, newspapers, the Internet, and other channels, consult relevant professional medical staff, understand the prevention methods and risk factors that are easy to cause falls, know the harm caused by “fall fear”, and establish the concept that “falls can be prevented”.
- The elderly should exercise appropriately. Instead of limiting their activities due to fear of falling, appropriate exercise can not only improve the body’s balance ability and strengthen the lower limb muscle strength, so as to prevent falling, but also effectively improve the fear of falling.
- The elderly should actively adjust their mentality. They can talk to professionals, relatives, and friends about their worries about falling down and seek help.